Healthcare Costs and Medical Financial Planning in the U.S
How to Protect Your Finances From Medical Expenses
Advertising
Healthcare is one of the most unpredictable—and expensive—parts of personal finance in the United States. Even people with solid incomes and health insurance can face significant financial stress from medical bills, deductibles, and unexpected care.
Understanding how the U.S. healthcare system works financially is essential for protecting your savings, avoiding medical debt, and building long-term financial resilience.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- Why healthcare is so expensive in the U.S.
- How to budget for medical expenses
- Health insurance vs. out-of-pocket costs
- How to prevent and manage medical debt
🏥 Why Healthcare Is So Expensive in the U.S.
The U.S. spends more on healthcare per person than any other developed country—yet costs are largely borne by individuals.
Key reasons healthcare is expensive:
- Private insurance–driven system rather than universal coverage
- High administrative and billing costs
- Expensive prescription drugs
- Lack of price transparency
- Fee-for-service care model (providers are paid per service, not outcome)
In many cases, patients don’t know the true cost of care until after receiving treatment—making budgeting especially difficult.
👉 Healthcare costs aren’t just high—they’re unpredictable, which makes financial planning essential.
📊 How to Budget for Medical Expenses
Medical expenses should be treated as a core budget category, not an afterthought.
Step 1: Know your baseline costs
Include:
- Monthly insurance premiums
- Prescription medications
- Ongoing treatments or therapy
- Routine care (checkups, dental, vision)
Step 2: Plan for variable and unexpected costs
Healthcare expenses fluctuate. Smart strategies include:
- Building a medical sinking fund
- Setting aside money monthly for out-of-pocket costs
- Separating healthcare savings from general emergency funds
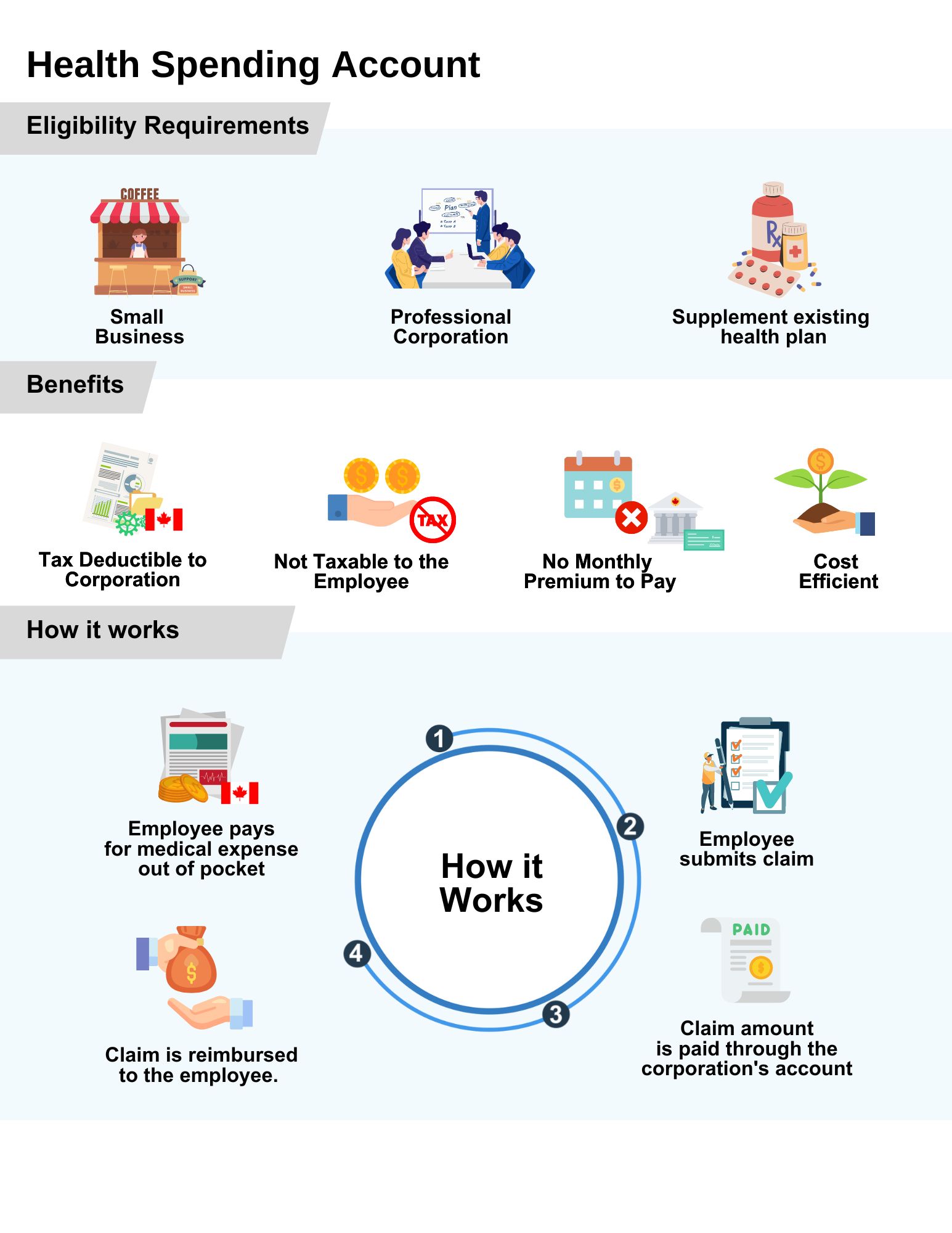
Step 3: Use tax-advantaged accounts when available
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) (for eligible plans)
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)
These accounts allow you to pay medical expenses with pre-tax dollars, reducing overall costs.
👉 Budgeting for healthcare isn’t pessimistic—it’s protective.
🧾 Health Insurance vs. Out-of-Pocket Costs
Health insurance doesn’t eliminate medical costs—it reshapes them.
Common health insurance cost components:
- Premium – Monthly cost of coverage
- Deductible – Amount you pay before insurance starts covering expenses
- Copays – Fixed fees for services
- Coinsurance – Percentage you pay after the deductible
- Out-of-pocket maximum – Your annual spending cap
The insurance vs. out-of-pocket tradeoff:
- Lower premiums often mean higher deductibles
- Higher premiums may reduce surprise expenses
- Uninsured or underinsured patients face the highest financial risk
👉 The best plan isn’t the cheapest—it’s the one that aligns with your health needs and financial capacity.
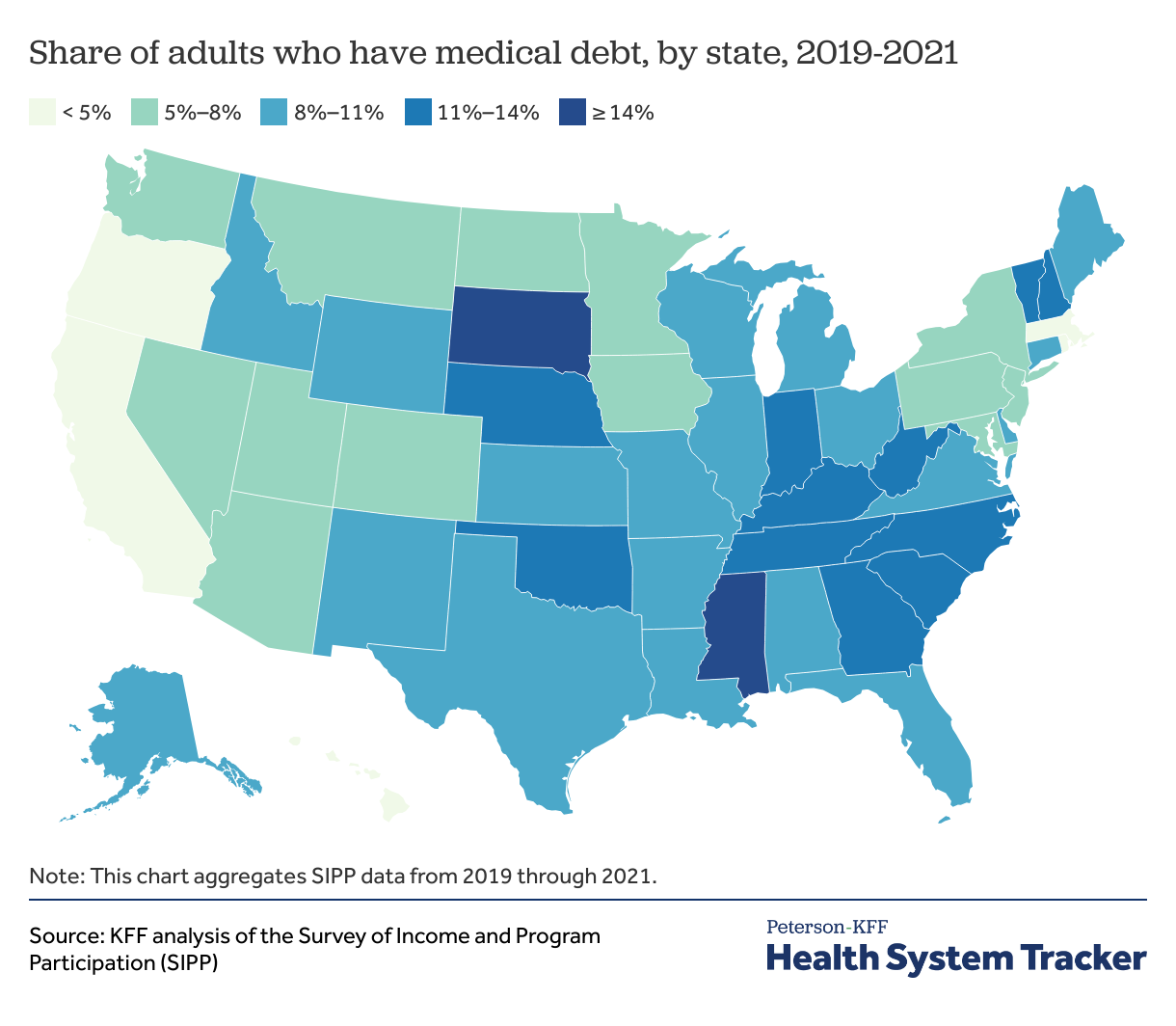
💸 Medical Debt: Prevention and Management
Medical debt is one of the most common forms of debt in the U.S.—and one of the least predictable.
How to prevent medical debt:
- Verify insurance coverage before procedures
- Ask for cost estimates upfront
- Use in-network providers whenever possible
- Review bills carefully for errors
- Negotiate payment plans early
Many hospitals and providers offer:
- Interest-free payment plans
- Financial assistance programs
- Discounts for prompt or cash payment
Managing existing medical debt:
- Do not ignore medical bills
- Contact providers to negotiate
- Ask about hardship programs
- Prioritize medical debt strategically alongside other obligations
👉 Medical debt doesn’t mean financial failure—it often reflects a system problem, not personal mismanagement.
🧠 Medical Costs and Long-Term Financial Planning
Healthcare costs don’t disappear over time—they often increase, especially in retirement.
Long-term planning should account for:
- Rising premiums and deductibles
- Chronic care needs
- Prescription costs
- Long-term care considerations
People who plan proactively are more likely to:
- Maintain emergency savings
- Avoid high-interest debt
- Make calmer decisions during health crises
- Protect retirement savings
👉 Medical planning is financial planning.
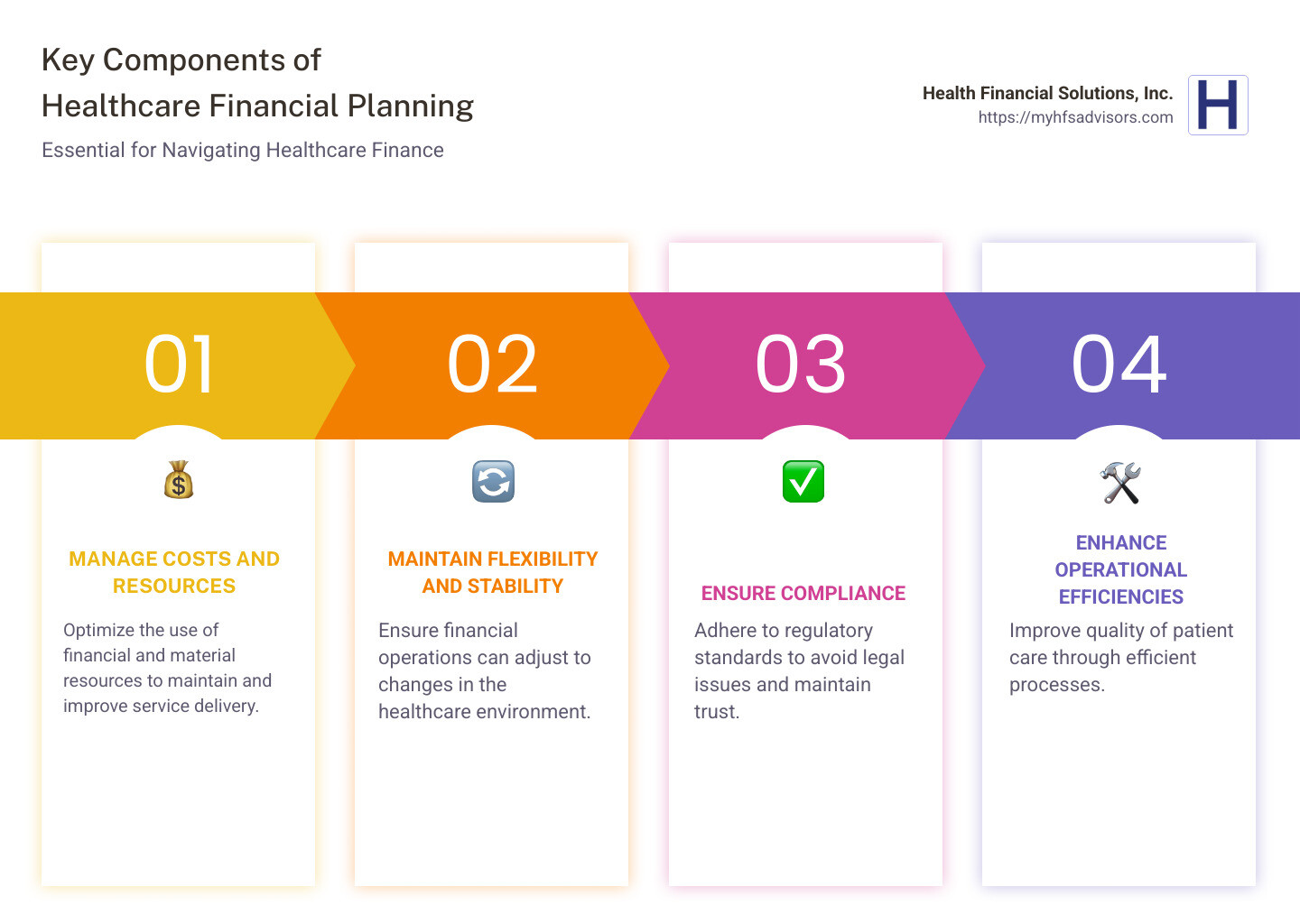
🛡️ Building Financial Resilience Around Healthcare
True financial resilience means being able to handle health-related expenses without derailing your life.
Key pillars include:
- Adequate insurance coverage
- Dedicated medical savingsUnderstanding your benefits
- Willingness to ask questions and negotiate
- Regular review of coverage and costs
Even small steps—like understanding your deductible or reviewing bills—can save thousands of dollars over time.
✅ Final Thoughts
Healthcare costs are a reality of life in the United States, but they don’t have to destroy your financial stability. By understanding why medical care is expensive, budgeting intentionally, choosing insurance wisely, and planning for out-of-pocket expenses, you can reduce stress and protect your long-term goals.
Medical expenses are often unavoidable—but financial chaos is not.
The most powerful healthcare financial strategy is preparation, not prediction.